Understanding the volleyball court size is essential for players, coaches, schools, sports academies, and facility owners. Whether you are planning a professional indoor court, an outdoor recreational court, or a training facility, using the official volleyball court dimensions ensures fair play, safety, and compliance with international standards.
This guide covers official volleyball court measurements, layouts, markings, and flooring requirements.
Table of contents
- Understanding Standard Volleyball Court Dimensions
- Court Segments Explained
- Comparison: Indoor vs Outdoor Volleyball Court
- Volleyball Court Surface & Material
- Common Measurement Mistakes to Avoid
- Beach Volleyball Court Dimensions
- Why Dimensions Differ Across Formats
- Volleyball Court Lines and Markings
- Volleyball Net Height and Pole Positioning
- Zones Within the Volleyball Court
- Space Requirements Around the Volleyball Court
- Technical Standards for Volleyball Court Flooring
- Expert Tips for Designing a Volleyball Court
- Conclusion
Understanding Standard Volleyball Court Dimensions
Standard volleyball court dimensions are defined by the FIVB (Fédération Internationale de Volleyball) to ensure fair and consistent gameplay worldwide. These measurements apply to both indoor and outdoor volleyball courts.
The official volleyball court measures 18 meters in length and 9 meters in width, creating a total playing area of 162 square meters. The court is divided into two equal halves of 9 × 9 meters by a center line, with a net placed directly above it.
A key feature of the court layout is the attack line, which is drawn 3 meters from the center line on each side. This line separates front-row and back-row players and plays an important role in game rules and player positioning.
Around the playing area, a free zone is required to allow players to move safely while chasing the ball. The minimum recommended free zone is 3 meters on all sides, although professional matches often use larger safety areas.
While the court size remains the same for indoor and outdoor volleyball, the flooring material differs. Indoor courts typically use wooden, PVC, or PU sports flooring, while outdoor courts often use synthetic acrylic flooring due to its durability and weather resistance.
Overall, understanding standard volleyball court dimensions helps ensure proper court construction, safe play, and compliance with official volleyball regulations.
Court Segments Explained
| Court Section | Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Playing Surface | 18 m × 9 m | Active match area |
| Half-Court | 9 m × 9 m | Each team’s side |
| Attack Zone | 3 m from center | Determines front/back row play |
| Free Zone | ≥ 3 m all around | Safety and movement |
| Clearance Height | ≥ 7 m | No overhead obstructions |
Comparison: Indoor vs Outdoor Volleyball Court
| Feature | Indoor Court | Outdoor Court |
|---|---|---|
| Court Dimensions | 18 m × 9 m | 18 m × 9 m |
| Surface | Wooden / PU / PVC | Acrylic / Cement / Grass |
| Free Zone Requirements | Stricter | Flexible (but recommended) |
| Weather Impact | Controlled | Sun, wind, rain |
The playing dimensions are identical — but outdoor courts require more attention to surface choice, drainage, and weather resistance.
Volleyball Court Surface & Material

The surface affects traction, safety, and performance. Standard materials include:
🔹 Indoor Courts
- PU (Polyurethane) Sports Flooring
Smooth, shock-absorbing, professional grade - PVC Sports Flooring
Good balance of durability and comfort
🔹 Outdoor Courts
- Synthetic Acrylic Sports Flooring
Weather-resistant, non-slip, long-lasting - Concrete or Asphalt Base + Acrylic Finish
Cost-effective & durable
Why proper flooring matters:
Good surface reduces injuries, improves ball bounce consistency, and enhances player comfort.
Common Measurement Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Why It’s a Problem |
|---|---|
| Incorrect court length or width | Invalid for competition |
| Incomplete free zone | Player injuries |
| Faded lines | Referee mistakes |
| Wrong net height | Unfair play |
Always use measuring tools, flat surfaces, and certified installers for accuracy.
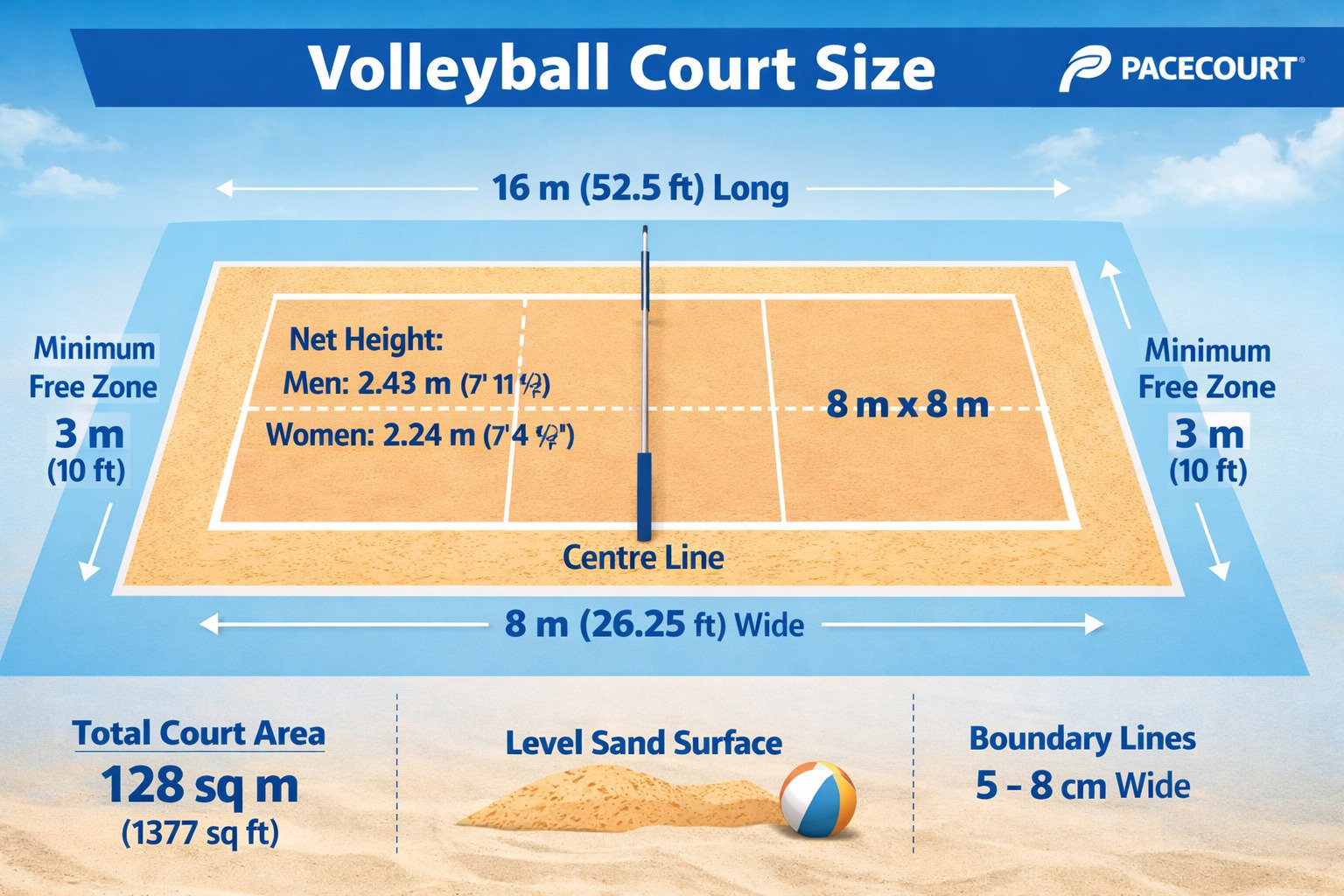
Beach Volleyball Court Dimensions
Beach volleyball court dimensions are different from indoor or standard volleyball courts and are regulated by the FIVB (Fédération Internationale de Volleyball) to ensure uniform play worldwide.
The official beach volleyball court size is 16 meters long and 8 meters wide, creating a total playing area of 128 square meters. This court is slightly smaller than an indoor volleyball court and is designed specifically for two-player teams.
The court is divided into two equal halves of 8 × 8 meters by a center line, with the net placed at the center. Unlike indoor volleyball, there is no attack line in beach volleyball, as all players can attack from anywhere on their side of the court.
A free zone surrounds the court to allow safe movement. The minimum free zone required is 3 meters on all sides, though professional tournaments often provide larger safety areas.
The playing surface must be level sand, with a minimum depth of 40 cm, free from stones or hard objects to prevent injuries. Court boundary lines are usually 5–8 cm wide and made of flexible material, secured to the sand.
Net Height for Beach Volleyball
- Men: 2.43 meters
- Women: 2.24 meters
In summary, beach volleyball court dimensions are carefully designed to support fast, athletic play while ensuring player safety and fairness in both recreational and professional matches.
Why Dimensions Differ Across Formats

Volleyball court dimensions differ across formats such as indoor volleyball, beach volleyball, and recreational or school-level play to match the playing environment, number of players, surface type, and game dynamics. These variations are intentional and help maintain fairness, safety, and competitive balance.
1. Playing Surface and Environment
Indoor volleyball is played on hard, smooth surfaces like wooden or synthetic flooring, allowing faster movement and controlled jumps. Beach volleyball is played on sand, which slows movement and increases physical effort. To balance this, beach volleyball courts are smaller in size, reducing the distance players must cover.
2. Number of Players
Indoor volleyball is played with six players per team, requiring more space for rotations, positioning, and coordinated attacks. Beach volleyball is played with two players per team, so a smaller court suits the reduced number of players while keeping rallies competitive.
3. Style and Pace of the Game
Indoor volleyball focuses on structured rotations, quick sets, and fast attacks, which benefit from a larger playing area. Beach volleyball emphasizes endurance, ball control, and adaptability, and a smaller court keeps the game intense despite slower movement on sand.
4. Safety Considerations
Court size and free-zone requirements are designed to reduce injury risk. On sand, players dive and fall more frequently, so the court is compact and cushioned. Indoor courts require more space around the playing area to allow safe movement at higher speeds.
5. Skill and Accessibility Levels
Recreational, school, or training courts may slightly adjust dimensions to fit available space and skill levels. This makes the sport more accessible without changing the core rules of play.
6. Standardization by Governing Bodies
Organizations like the FIVB set different standards to preserve the unique identity of each volleyball format, ensuring consistency in competitions while adapting to environmental and gameplay needs.
Volleyball Court Lines and Markings
Volleyball court lines and markings define the playing area, player positions, and movement zones during a match. Accurate line markings are essential for fair play, correct officiating, and compliance with official volleyball rules set by the FIVB (Fédération Internationale de Volleyball).
1. Boundary Lines
Boundary lines mark the outer limits of the volleyball court.
- Sidelines: Run along the length of the court
- End lines (baselines): Run along the width of the court
- All boundary lines are 5 cm wide
- Lines are included within the court dimensions
These lines determine whether the ball is in or out during play.
2. Center Line
The center line runs beneath the net and divides the court into two equal halves.
- Each half measures 9 m × 9 m
- Players must not cross completely into the opponent’s court
- Partial foot contact over the line is allowed if it does not interfere with play
3. Attack Line (3-Meter Line)
The attack line is drawn 3 meters from the center line on both sides of the court.
- Separates front-row and back-row players
- Back-row players must take off from behind this line when attacking the ball above net height
- Critical for enforcing rotation and attack rules
4. Service Zone
The service zone is located behind each end line.
- Extends the full width of the court
- Server must stand behind the end line during the serve
- No fixed depth, but must remain within the extension of the sidelines
5. Substitution Zone
- Located between the attack line and center line near the scorer’s table
- Used for legal player substitutions during the match
- Important for match officials and team rotations
6. Libero Replacement Zone
- Positioned between the attack line and end line
- Used for libero player replacements
- Ensures smooth and legal player exchanges
7. Free Zone Markings
The free zone surrounds the court and provides safety space.
- Minimum 3 meters on all sides
- Marked visually but not considered part of the playing court
- Prevents collisions with walls, benches, or officials
8. Line Color and Visibility
- Lines should be light-colored (usually white or yellow)
- Must clearly contrast with the playing surface
- Should be non-slip and durable, especially on synthetic flooring
Importance of Accurate Court Markings
✔ Ensures fair officiating
✔ Maintains player safety
✔ Supports official competitions
✔ Enhances game flow and clarity
Poor or faded markings can lead to disputes and incorrect decisions during matches.
Volleyball Net Height and Pole Positioning

Correct volleyball net height and pole positioning are essential for fair gameplay, player safety, and compliance with official rules. These standards are set by the FIVB (Fédération Internationale de Volleyball) and apply to both indoor and outdoor volleyball courts.
Standard Volleyball Net Height
The official net height varies based on the category of play:
- Men’s Volleyball: 2.43 meters (7 feet 11⅝ inches)
- Women’s Volleyball: 2.24 meters (7 feet 4⅛ inches)
- Youth Volleyball: Varies by age group, typically between 2.10 and 2.35 meters
The net height is measured at the center of the court, and the height at both sides of the net must not exceed the center height by more than 2 centimeters.
Volleyball Net Specifications
- Net width (height): 1 meter
- Net length: Approximately 9.5 to 10 meters
- Mesh size: 10 cm square
- Top band: White canvas band, 7 cm wide
The net must be tightly secured to ensure proper tension and consistent ball rebound.
Pole Positioning for Volleyball Nets
Correct pole placement is critical for maintaining net tension and ensuring player safety.
- Poles are placed outside the sidelines
- Distance from sidelines: 0.5 to 1 meter
- Poles must be padded to prevent injuries
- Poles should be smooth and rounded with no sharp edges
This positioning keeps the poles out of the playing area while maintaining net stability.
Antennas and Their Placement
- Two antennas are fixed to the net above each sideline
- Antennas extend 80 cm above the net
- They mark the legal crossing space for the ball
Antennas are an important visual reference for referees and players.
Indoor vs Outdoor Net Setup
| Feature | Indoor Volleyball | Outdoor Volleyball |
|---|---|---|
| Pole type | Fixed or adjustable | Removable or anchored |
| Padding | Mandatory | Highly recommended |
| Wind impact | None | Must be considered |
| Net tension | High and consistent | Slightly flexible |
Outdoor installations must account for wind and weather conditions when setting tension.
Zones Within the Volleyball Court
The zones within a volleyball court define player positions, movement rules, and gameplay responsibilities. These zones are established by official volleyball regulations to ensure fair play, correct rotations, and smooth match flow.
1. Front Zone (Attack Zone)
The front zone, also called the attack zone, is the area between the center line and the attack line (3-meter line).
- Depth: 3 meters from the center line
- Used by front-row players
- Only front-row players can attack the ball above net height from this zone
- Blocking is permitted only for front-row players
2. Back Zone
The back zone is the area between the attack line and the end line.
- Used by back-row players
- Back-row players must jump from behind the attack line when attacking above the net
- Important for enforcing rotation and attack rules
3. Service Zone
The service zone is located behind the end line on each side of the court.
- Extends across the full width of the court
- The server must stand within this zone while serving
- No fixed depth, but the server must remain behind the end line
4. Substitution Zone
- Located between the center line and attack line near the scorer’s table
- Used for official player substitutions
- Helps referees manage team rotations and substitutions efficiently
5. Libero Replacement Zone
- Positioned between the attack line and end line
- Used exclusively for libero replacements
- Allows smooth and legal entry and exit of the libero player
6. Free Zone
The free zone surrounds the playing court and provides safety space.
- Minimum 3 meters on all sides
- Players may enter this zone to retrieve the ball
- Not considered part of the playing court
7. Playing Court
- Measures 18 meters × 9 meters
- Includes all boundary lines
- Divided equally into two 9 × 9 meter halves
Importance of Court Zones
✔ Ensures correct player positioning
✔ Maintains fair rotations
✔ Supports accurate officiating
✔ Enhances player safety
Each zone plays a specific role in regulating how the game is played.
Space Requirements Around the Volleyball Court
Proper space requirements around a volleyball court are essential for player safety, smooth gameplay, and compliance with official volleyball standards. This surrounding area is known as the free zone and is just as important as the playing court itself.
What Is the Free Zone?
The free zone is the clear space surrounding the volleyball playing court that allows players to move freely while chasing the ball, serving, or defending without risk of injury.
Minimum Space Requirements
According to official guidelines:
- Minimum free zone: 3 meters on all sides of the court
- Applies to school, recreational, and standard competitive play
This means the minimum total area required is approximately 24 meters × 15 meters.
Recommended Space for Professional Matches
For national and international competitions, larger safety areas are advised:
- Sidelines: 5 meters
- End lines: 6.5 to 8 meters
- Overhead clearance: Minimum 7 meters, higher for elite events
Larger free zones improve player safety and allow for more dynamic play.
Indoor Volleyball Space Requirements
Indoor courts require additional considerations:
- No pillars, lighting, or fixtures above the court
- Adequate space for referee stands, benches, and scorer’s table
- Proper ventilation and lighting without glare
Outdoor Volleyball Space Requirements
Outdoor courts need:
- Extra space for wind movement
- Proper drainage around the court
- Safe distance from walls, fences, and seating areas
Why Free Zone Space Is Important
✔ Prevents player injuries
✔ Allows full-range movement
✔ Supports official match regulations
✔ Improves overall playing experience
Insufficient space can lead to dangerous collisions and interrupted play.
Technical Standards for Volleyball Court Flooring

Technical standards for volleyball court flooring are designed to ensure player safety, consistent performance, and compliance with national and international regulations. Proper flooring directly affects traction, shock absorption, ball bounce, and injury prevention, making it a critical component of any volleyball court.
1. Surface Performance Requirements
Volleyball court flooring must meet the following performance criteria:
- Slip resistance: Provides secure footing without restricting movement
- Shock absorption: Reduces impact stress on joints and muscles
- Uniform ball bounce: Ensures predictable and fair gameplay
- Surface flatness: No uneven areas that could cause injuries
These factors help maintain high-quality play and reduce fatigue.
2. Approved Flooring Types
Indoor Volleyball Flooring
- PU (Polyurethane) Sports Flooring
Preferred for professional indoor courts due to excellent shock absorption and durability. - PVC Sports Flooring
Common in schools and training centers for comfort and easy maintenance. - Wooden Sports Flooring
Traditional option for indoor arenas with proper sub-base preparation.
Outdoor Volleyball Flooring
- Synthetic Acrylic Flooring
Weather-resistant, non-slip, and ideal for outdoor and multipurpose courts. - Concrete or Asphalt Base with Acrylic Finish
Cost-effective and durable for long-term outdoor use.
3. Thickness and Layer System
Volleyball flooring systems typically consist of:
- A stable sub-base (concrete or asphalt)
- Cushion or elastic layers for shock absorption
- Top wear layer for grip and durability
Proper layering ensures consistent performance and longevity.
4. Safety and Injury Prevention Standards
Flooring must:
- Minimize surface friction extremes
- Prevent excessive hardness
- Support controlled sliding and quick directional changes
High-quality sports flooring significantly reduces the risk of ankle, knee, and lower-back injuries.
5. Line Marking Standards
- Lines must be 5 cm wide
- Color should contrast clearly with the floor surface
- Markings must be durable and non-slip
- Paint or markings should not affect surface traction
6. Indoor Environmental Requirements
For indoor courts:
- Proper ventilation to control humidity
- Adequate lighting without glare
- Stable temperature to prevent floor expansion or contraction
Environmental control helps maintain surface integrity.
7. Maintenance and Durability
A standard volleyball court flooring system should:
- Resist wear from frequent use
- Be easy to clean and maintain
- Retain grip and color over time
Regular maintenance extends floor life and ensures continued safety.
Expert Tips for Designing a Volleyball Court
Designing a volleyball court requires more than just marking dimensions. Proper planning ensures player safety, optimal performance, durability, and compliance with official standards. Below are expert tips to help you design a high-quality volleyball court for schools, academies, clubs, or professional use.
1. Follow Official Court Dimensions
Always start with standard volleyball court dimensions (18 m × 9 m). Accurate measurements ensure fair play and allow the court to be used for official matches, training, and tournaments.
2. Provide Adequate Free Zone Space
Ensure a minimum 3-meter free zone around the court. For competitive or professional use, increase this space to improve safety and allow dynamic movement.
3. Choose the Right Flooring System
Select flooring based on court location:
- Indoor courts: PU, PVC, or wooden sports flooring
- Outdoor courts: Synthetic acrylic flooring with proper drainage
The surface should be non-slip, shock-absorbing, and durable.
4. Ensure Proper Drainage (Outdoor Courts)
Outdoor volleyball courts must have efficient drainage to prevent water accumulation. A slight slope and quality base layers help protect the surface and extend court life.
5. Maintain Correct Net Height and Pole Placement
Install the net at the correct height for the intended category (men, women, or youth). Poles should be placed 0.5–1 meter outside the sidelines and padded for safety.
6. Use High-Visibility Line Markings
Court lines should be:
- 5 cm wide
- Clearly visible against the floor color
- Made with non-slip, long-lasting materials
Clear markings support accurate officiating and gameplay.
7. Plan Lighting Carefully
For indoor courts, use evenly distributed lighting without glare. Outdoor courts should have sufficient illumination for evening play, positioned to avoid shadows on the court.
8. Allow Proper Overhead Clearance
Ensure a minimum ceiling height of 7 meters for indoor courts. This prevents interference during serves and high ball play.
9. Prioritize Player Safety
Include padding on poles, smooth surface transitions, and safe distances from walls, fences, or seating areas to reduce injury risk.
10. Design for Multi-Purpose Use
If space allows, design the court to support multiple sports by using compatible flooring and removable equipment. This increases usability and return on investment.
Conclusion
Designing a volleyball court requires careful attention to dimensions, zoning, safety spaces, net positioning, and flooring quality. When all these elements are planned correctly, the result is a court that supports fair play, reduces injury risk, and delivers consistent performance for players at every level. From accurate measurements and proper free zones to durable surfaces and clear line markings, every detail plays a role in creating a professional-standard volleyball court.
With Pacecourt, you get more than just materials—you get expert guidance, high-quality synthetic sports flooring systems, and solutions designed to meet official volleyball standards. Whether you are building an indoor court, an outdoor facility, or a multipurpose sports area, Pacecourt’s proven flooring technology and industry expertise ensure long-lasting performance, safety, and international-level playability. Choosing Pacecourt means investing in a volleyball court built for excellence.





