Basketball court size plays a defining role in how the game is played, experienced, and enjoyed at every level. From professional arenas filled with roaring crowds to quiet backyard courts designed for family fun, court dimensions influence player movement, strategy, spacing, and overall performance. We often underestimate how much precision goes into designing a basketball court, yet every line, angle, and measurement exists for a reason. Standardization ensures fairness, safety, and consistency, whether the game is played in a global championship or a local school gymnasium.
Understanding basketball court dimensions is essential for players, coaches, architects, facility managers, and enthusiasts alike. A correctly measured court supports proper gameplay, reduces injury risks, and aligns with official regulations. While casual players may focus on shooting hoops, professionals rely on exact court layouts to execute plays with pinpoint accuracy. Even a slight deviation in markings or spacing can change how the game flows.
Basketball courts are governed by different organizations, each with its own standards. The NBA, FIBA, NCAA, and NFHS establish precise rules for court size and markings. These variations, though subtle, significantly impact gameplay. Knowing the differences helps in designing courts that meet specific competitive or recreational needs. As basketball continues to grow globally, understanding these standards becomes increasingly valuable for modern facilities and aspiring players worldwide.
Table of contents
- History and Evolution of Basketball Court Sizes
- Standard Basketball Court Size Overview
- NBA Basketball Court Dimensions Explained
- FIBA Basketball Court Size and Specifications
- NCAA and High School Basketball Court Dimensions
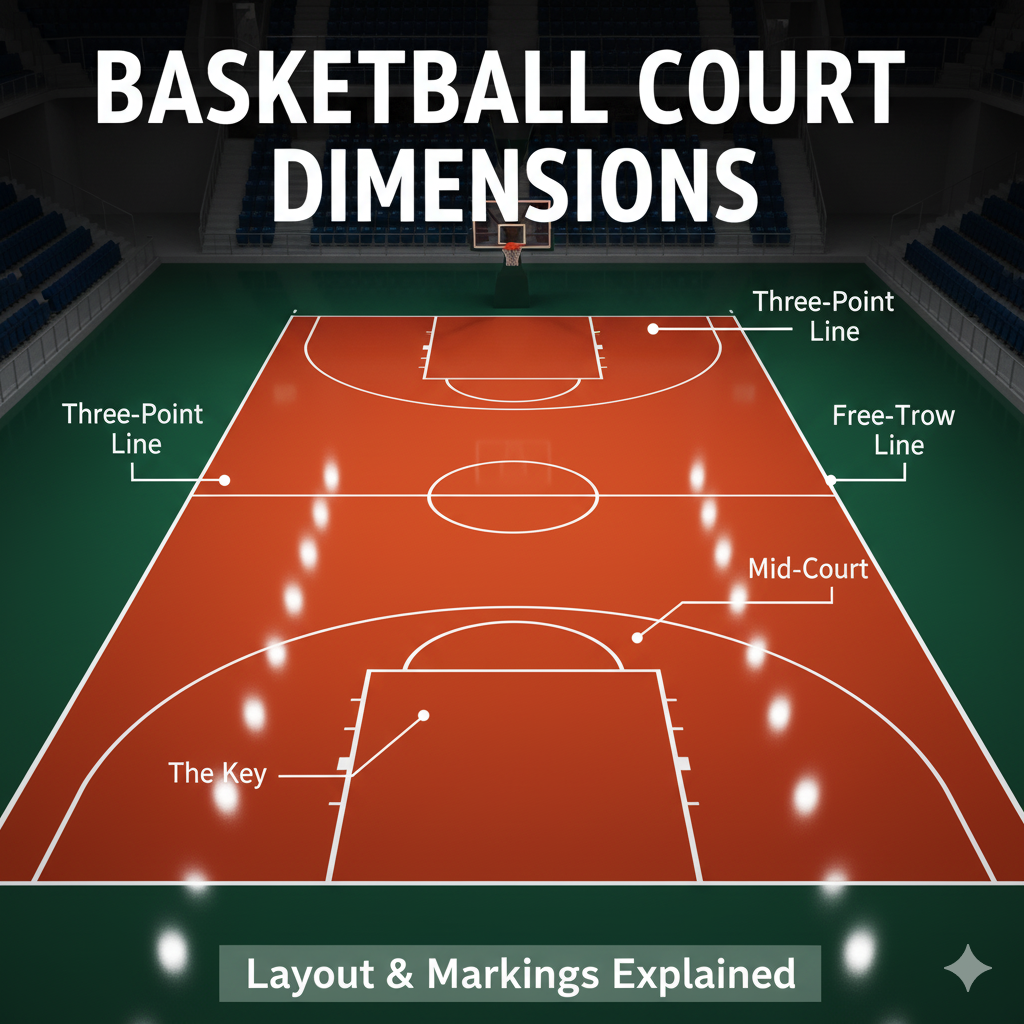
- Basketball Court Markings Explained
- Indoor vs Outdoor Basketball Court Sizes
- Basketball Court Flooring and Surface Considerations
- Common Basketball Court Size Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion
History and Evolution of Basketball Court Sizes
The evolution of basketball court size reflects the growth and professionalization of the sport itself. When basketball was invented in 1891, games were played in small gymnasiums with improvised layouts. There were no standardized dimensions, and court sizes varied widely depending on available space. As basketball gained popularity, the need for consistent playing conditions became evident, prompting the establishment of formal measurements.
Early courts were often smaller, leading to congested gameplay and limited movement. As athleticism increased and strategies evolved, larger courts became necessary to accommodate faster pacing and dynamic playstyles. The introduction of dribbling, fast breaks, and perimeter shooting influenced how courts were designed. Over time, governing bodies introduced precise regulations to maintain fairness and enhance the spectator experience.
Professional leagues further refined court dimensions to showcase elite athletic performance. The NBA introduced wider lanes and longer three-point lines to balance scoring and defense. International organizations like FIBA adopted slightly different measurements to suit global play styles and facility constraints. These changes reflect ongoing efforts to optimize the game while preserving its core principles.
Today’s basketball courts represent decades of refinement. Each measurement is the result of testing, feedback, and adaptation. Understanding this evolution helps us appreciate why modern basketball courts are designed with such exacting standards and why adherence to these dimensions remains critical for competitive integrity.
Standard Basketball Court Size Overview
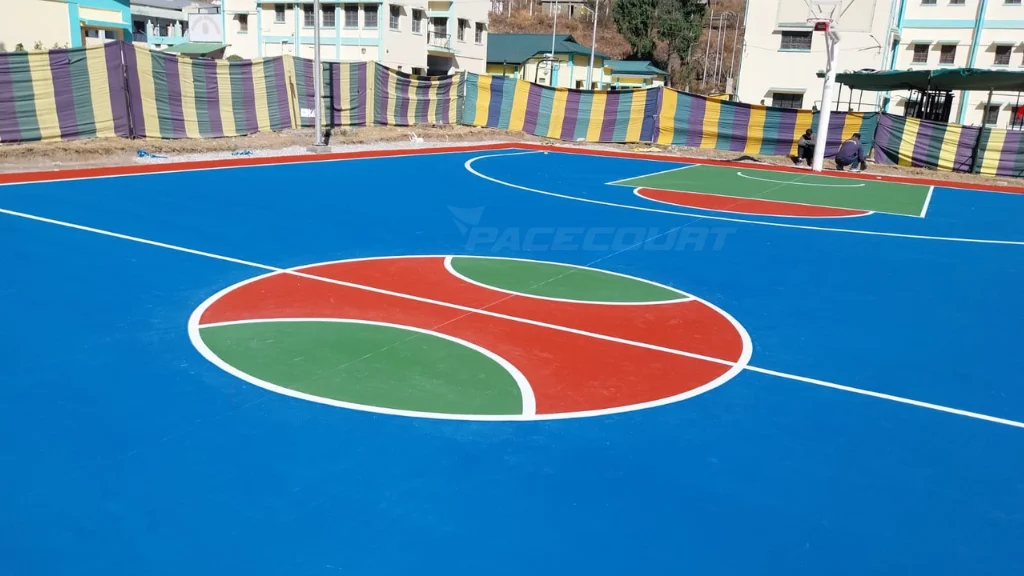

A standard basketball court is rectangular, designed to provide ample space for movement, strategy, and fair competition. While dimensions vary slightly depending on governing bodies, the overall structure remains consistent. The court includes a playing area, boundary lines, and clearly defined zones that dictate gameplay rules.
Professional courts are typically 94 feet long and 50 feet wide, offering maximum space for elite competition. Amateur and recreational courts may be smaller, but they still follow proportional layouts to maintain a balanced playing experience. These dimensions ensure players can perform fundamental actions such as passing, shooting, and defending without spatial limitations.
Standardization benefits players at all levels by creating familiarity. When athletes transition from school-level play to professional leagues, consistent court layouts reduce adaptation time. Facility designers rely on these standards to build courts that meet regulatory approval and enhance usability.
Beyond length and width, standard courts also specify distances for key markings, including the free throw line, three-point arc, and center circle. Each element contributes to the rhythm and structure of the game. A well-designed court supports smooth gameplay, accurate officiating, and an enjoyable experience for players and spectators alike.
NBA Basketball Court Dimensions Explained
NBA basketball courts represent the gold standard of professional play. The official NBA court size is 94 feet long and 50 feet wide, providing the largest playing surface among major basketball organizations. This expansive layout supports fast-paced gameplay, spacing for perimeter shooting, and dynamic offensive strategies.
The free throw lane, commonly known as the key, measures 16 feet wide, allowing room for post play and rebounding battles. The three-point line extends 23 feet 9 inches from the basket at the top of the arc, while the corners measure 22 feet, creating strategic shooting zones. These measurements influence shot selection and defensive coverage.
The center circle has a 12-foot diameter, facilitating fair jump ball situations. The restricted area, marked by a semicircle under the basket, helps officials determine charging and blocking fouls. Every line on an NBA court is precisely measured and painted to exact specifications.
NBA courts also feature consistent line widths, typically 2 inches, ensuring visibility and uniformity. These details may seem minor, but they contribute to the professional polish and fairness expected at the highest level of basketball competition.
FIBA Basketball Court Size and Specifications
FIBA basketball courts serve as the international standard, used in global competitions and most countries outside North America. A FIBA court measures 91.86 feet long and 49.21 feet wide, slightly smaller than an NBA court. These dimensions accommodate international facilities while maintaining competitive integrity.
The three-point line in FIBA competitions is set at 22 feet 1.75 inches, encouraging balanced scoring between perimeter and interior play. The free throw lane remains 16 feet wide, similar to NBA standards, ensuring consistency in post play. The center circle measures 11.81 feet in diameter, slightly smaller but functionally equivalent.
FIBA courts emphasize versatility and accessibility. Their dimensions allow for efficient use of space in multi-purpose arenas and community facilities. Despite minor differences, FIBA courts uphold the same principles of fairness, safety, and performance optimization.
Understanding FIBA specifications is crucial for international tournaments, training facilities, and players competing across borders. These standards ensure seamless transitions between domestic and global competitions.
NCAA and High School Basketball Court Dimensions
College and high school basketball courts are designed to bridge the gap between recreational play and professional competition. NCAA courts measure 94 feet by 50 feet, matching NBA dimensions, while high school courts typically follow similar layouts with slight variations in markings.
The three-point line in college basketball is set at 22 feet 1.75 inches, aligning with international standards. High school courts use a shorter three-point distance, promoting skill development and balanced gameplay for younger athletes. The free throw line remains 15 feet from the backboard across all levels, ensuring consistency in shooting mechanics.
These courts prioritize player development, safety, and accessibility. Clear markings and standardized dimensions help young athletes build foundational skills while preparing for higher levels of competition. Educational institutions rely on these standards to create versatile facilities that support multiple sports and activities.
Basketball Court Markings Explained
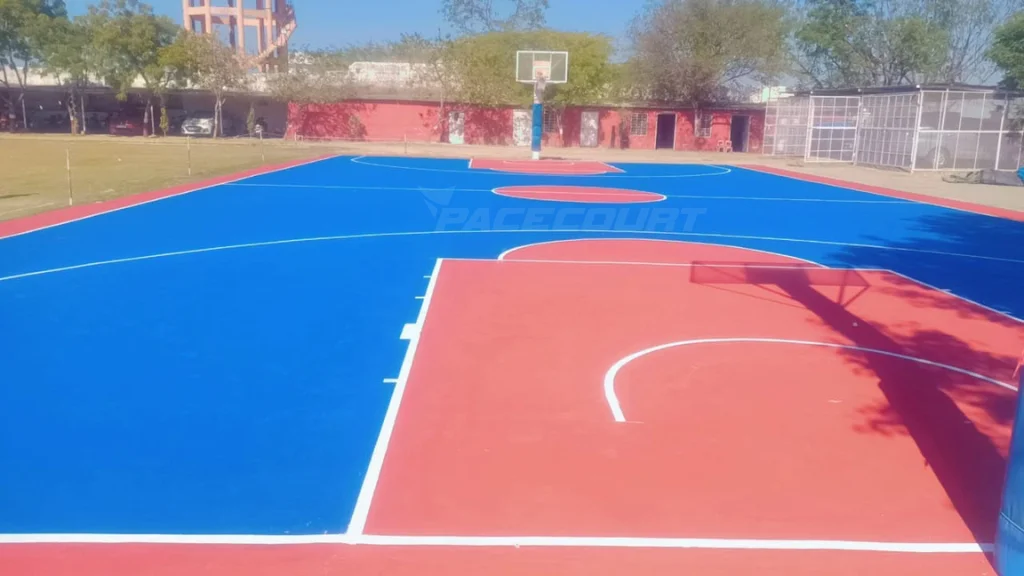

Basketball court markings define how the game is played. Each line serves a specific purpose, guiding player movement and officiating decisions. The center line divides the court into two equal halves, while the center circle facilitates jump balls. Boundary lines establish the playable area and out-of-bounds limits.
The free throw lane dictates player positioning during free throws, ensuring fairness and spacing. The three-point line rewards long-range shooting, adding strategic depth to the game. The restricted area helps officials enforce charging and blocking rules, enhancing player safety.
Line accuracy is critical. Misaligned markings can lead to disputes, confusion, and unfair advantages. Properly painted lines enhance visibility, reduce errors, and support smooth gameplay. Whether designing a professional arena or a community court, understanding these markings is essential.
Indoor vs Outdoor Basketball Court Sizes
Indoor and outdoor basketball courts often share similar dimensions, but their construction and materials differ significantly. Indoor courts adhere strictly to official standards, providing controlled environments for competitive play. Outdoor courts may vary slightly to accommodate available space and environmental factors.
Outdoor courts often prioritize durability and accessibility. While dimensions may remain close to standard sizes, surface materials and line visibility are adapted for weather resistance. Indoor courts focus on performance, using hardwood flooring and precise measurements to optimize play.
Both court types serve important roles in basketball development. Understanding their differences helps facility planners and players choose the right environment for their needs.
Basketball Court Flooring and Surface Considerations

Basketball court flooring is one of the most critical elements influencing player performance, safety, durability, and overall game quality. While court dimensions and markings define how the game is played, the surface beneath the players’ feet determines how the game feels. From professional arenas to school gyms, outdoor parks, and backyard courts, flooring choices directly affect traction, ball bounce, shock absorption, and long-term maintenance. Selecting the right basketball court surface is not a cosmetic decision; it is a functional and performance-driven requirement.
Different levels of play demand different flooring solutions. Professional and collegiate basketball prioritize precision, consistency, and injury prevention, while recreational and outdoor courts focus on durability, weather resistance, and cost efficiency. Understanding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each flooring type ensures the court meets its intended purpose without compromising player safety or gameplay quality.
Importance of Basketball Court Flooring
Basketball is a high-impact sport involving constant sprinting, jumping, sudden stops, and rapid changes in direction. The flooring must absorb shock efficiently to reduce stress on joints while maintaining enough firmness to support explosive movements. Poor flooring can increase the risk of injuries such as ankle sprains, knee strain, shin splints, and long-term joint damage.
Beyond safety, flooring influences game consistency. A quality surface provides predictable ball bounce, uniform traction, and reliable footing. Players instinctively adapt to how the floor responds, and inconsistencies can disrupt timing, shooting accuracy, and defensive reactions. For competitive environments, even minor surface irregularities can alter outcomes.
Facility managers also consider longevity and maintenance. Basketball courts experience heavy foot traffic, repeated impacts, and constant friction. The right flooring reduces maintenance costs, withstands wear, and maintains performance standards over time.
Hardwood Flooring for Indoor Basketball Courts
Hardwood flooring is the gold standard for indoor basketball courts, especially in professional, collegiate, and high-level school settings. Maple wood is the most commonly used material due to its strength, durability, and fine grain structure. Maple provides the ideal balance between hardness and elasticity, making it perfectly suited for basketball.
Hardwood courts are typically installed as floating systems, meaning the floor rests on shock-absorbing pads or subfloor structures. This design allows slight movement, reducing impact forces on players’ bodies. The result is improved comfort, reduced fatigue, and enhanced injury prevention.
Advantages of hardwood basketball flooring include:
- Consistent ball bounce
- Excellent traction
- Superior shock absorption
- Professional-grade appearance
- Long lifespan with proper maintenance
However, hardwood courts require controlled indoor environments. They are sensitive to moisture, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. Maintenance involves regular cleaning, periodic refinishing, and strict moisture control. Despite higher installation and upkeep costs, hardwood remains unmatched in performance quality for competitive play.
Synthetic Basketball Court Flooring
Synthetic flooring has become a popular alternative to hardwood, particularly in multi-purpose gyms and training facilities. These surfaces are typically made from vinyl, polyurethane, or rubber-based materials engineered to mimic the performance of hardwood while offering greater versatility.
Synthetic basketball floors provide consistent traction and shock absorption while being more resistant to moisture and temperature changes. This makes them suitable for facilities that host multiple sports or events. Unlike hardwood, synthetic surfaces often require less maintenance and do not need refinishing.
Key benefits of synthetic basketball court flooring include:
- Moisture resistance
- Lower maintenance requirements
- Durability under heavy use
- Customizable designs and colors
- Multi-sport compatibility
While modern synthetic floors perform well, some players still prefer the feel of traditional hardwood. Ball bounce and foot response may differ slightly, but high-quality synthetic systems continue to close the gap, making them a practical choice for schools and community centers.
Concrete Basketball Court Surfaces
Concrete is one of the most common materials used for outdoor basketball courts due to its affordability and durability. It provides a solid, long-lasting base that can withstand weather exposure, heavy use, and minimal maintenance. Concrete courts are widely found in parks, playgrounds, and residential areas.
Despite its durability, concrete is extremely rigid and offers little to no shock absorption. This increases the physical strain on players, particularly during extended play. Injuries related to joint stress are more common on concrete surfaces, especially without proper footwear.
To improve performance and safety, concrete courts are often coated with acrylic or polyurethane surface layers. These coatings enhance traction, improve ball bounce, and provide limited cushioning while also protecting the concrete from cracking and wear.
Asphalt Basketball Court Flooring
Asphalt is another widely used outdoor basketball court surface, particularly in public recreational spaces. It offers slightly more flexibility than concrete, which can reduce impact stress marginally. Asphalt is also faster to install and easier to repair in large outdoor areas.
However, asphalt surfaces can soften in extreme heat and become brittle in cold conditions. Over time, cracks and uneven areas may develop, affecting ball bounce and player safety. Like concrete, asphalt courts benefit greatly from protective surface coatings designed specifically for basketball play.
Asphalt courts are best suited for casual and recreational use rather than competitive environments. Proper drainage and regular maintenance are essential to extend their lifespan and usability.
Modular Sports Flooring Systems
Modular basketball court flooring systems are increasingly popular for both indoor and outdoor use. These interlocking tiles are typically made from high-impact polypropylene or similar materials. Modular systems are easy to install, customizable, and portable, making them ideal for temporary courts or multi-use spaces.
Advantages of modular basketball flooring include:
- Excellent traction
- Built-in drainage for outdoor use
- Shock absorption
- Quick installation and replacement
- Custom court designs and logos
Modular flooring provides a consistent playing experience and reduces stress on joints compared to bare concrete or asphalt. While not typically used in professional leagues, modular systems are highly effective for schools, training facilities, and backyard courts.
Outdoor Basketball Court Surface Coatings
Surface coatings play a vital role in enhancing outdoor basketball courts. Acrylic-based coatings are the most common choice due to their durability, slip resistance, and UV stability. These coatings improve ball bounce, protect the base material, and create a visually defined playing area.
High-quality coatings also help regulate surface temperature and reduce glare. Multiple layers are applied to ensure even texture and long-term performance. Choosing the right coating system significantly extends the lifespan of outdoor courts while improving safety and playability.
Traction, Grip, and Player Safety
Traction is a defining factor in basketball court flooring. Players rely on grip for quick cuts, explosive acceleration, and controlled stops. Too much traction increases injury risk by preventing natural foot rotation, while too little traction leads to slipping and loss of control.
Well-designed basketball flooring strikes a balance, allowing controlled movement without excessive resistance. Surface texture, material composition, and finish all influence traction levels. Regular maintenance is essential to preserve grip, as dust and debris can quickly reduce surface effectiveness.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Each flooring type has unique maintenance requirements. Hardwood courts demand routine cleaning and refinishing, while synthetic and modular surfaces require periodic inspection and basic upkeep. Outdoor courts benefit from regular cleaning, crack repairs, and recoating.
Investing in the right flooring from the beginning reduces long-term costs and ensures consistent performance. Facilities that prioritize maintenance enjoy safer courts, longer surface lifespan, and improved player satisfaction.
Common Basketball Court Size Mistakes to Avoid

Designing or constructing a basketball court may appear straightforward, but even small errors in sizing and layout can significantly affect gameplay, safety, and long-term usability. Basketball is a precision-based sport where spacing, angles, and distances matter. When court dimensions are incorrect or poorly planned, the result is often compromised performance, increased injury risk, and non-compliance with official standards. Whether the court is intended for professional competition, school use, recreational play, or a private residence, avoiding common basketball court size mistakes is essential.
Understanding these frequent errors helps ensure that the court delivers a consistent playing experience while meeting regulatory and functional requirements. Below, we outline the most common basketball court sizing mistakes and how they impact players and facilities.
Using Incorrect Court Length and Width
One of the most frequent mistakes is failing to match the correct court length and width to the intended level of play. Professional, collegiate, high school, and recreational courts all have different dimensional standards. Designing a court that is too short or too narrow alters spacing, reduces play flow, and limits strategic movement.
Incorrect overall dimensions can lead to:
- Congested gameplay
- Reduced fast-break opportunities
- Limited defensive spacing
- Difficulty adapting to regulation courts later
This mistake often occurs when space constraints are not properly evaluated during planning. Even recreational courts benefit from proportionally accurate dimensions, as this preserves the natural rhythm of the game.
Improper Three-Point Line Placement
The three-point line is one of the most critical markings on a basketball court, and misplacing it is a common error. Using the wrong distance for the level of play can drastically alter shooting dynamics. A line that is too close inflates scoring, while one that is too far discourages perimeter shooting.
Mistakes often include:
- Mixing NBA, FIBA, NCAA, and high school distances
- Incorrect corner three-point spacing
- Uneven arc curvature
Accurate three-point line placement ensures balanced offense and defense while maintaining consistency for players developing shooting mechanics.
Incorrect Free Throw Lane Dimensions
The free throw lane, or key, must be correctly sized to maintain fairness during free throws and post play. An improperly sized lane affects rebounding position, defensive alignment, and referee enforcement.
Common errors include:
- Lane width that is too narrow or too wide
- Incorrect distance from the free throw line to the backboard
- Misaligned lane markings
These mistakes disrupt player positioning and can lead to frequent violations during organized play. Proper lane dimensions are essential for both rule compliance and gameplay integrity.
Inaccurate Center Circle Measurements
The center circle is often overlooked, yet its size is critical for fair jump ball situations. A center circle that is too small restricts player movement during tip-offs, while an oversized circle creates unnecessary spacing.
Errors in center circle dimensions usually result from estimation rather than precise measurement. In regulated play, even minor deviations can affect officiating and fairness. Accurate center circle layout ensures equal opportunity during game starts and possession changes.
Ignoring Boundary Line Clearance Space
A major planning mistake involves failing to include adequate clearance space beyond boundary lines. Basketball requires room for player momentum, officiating movement, and spectator safety. Courts built too close to walls, fences, or obstacles increase injury risk.
Insufficient clearance leads to:
- Dangerous collisions
- Limited officiating visibility
- Restricted player movement
- Non-compliance with safety standards
Proper court design always includes additional space beyond the sidelines and baselines to ensure safe gameplay.
Incorrect Line Width and Visibility
Basketball court lines must be clearly visible and consistently sized. Using line widths that are too thin or too thick can confuse players and officials. Faded or poorly contrasting lines reduce clarity, especially under indoor lighting or outdoor sunlight.
Mistakes in line visibility often occur due to improper paint selection or lack of maintenance. Clear, uniform lines improve decision-making, reduce disputes, and enhance overall court usability.
Mismatched Proportions in Half-Court Designs
Half-court basketball layouts are popular for training and recreational use, but incorrect proportions are a common issue. Simply cutting a full court in half without adjusting key measurements results in distorted spacing.
Common half-court mistakes include:
- Incorrect three-point arc radius
- Improper lane positioning
- Misaligned center markings
A properly designed half-court maintains correct angles and distances, allowing players to practice realistic game scenarios.
Overlooking Ceiling Height and Vertical Clearance
While often associated with facility construction rather than court size, vertical clearance is an essential dimension. Insufficient ceiling height interferes with high-arcing shots, rebounds, and lob passes.
This mistake limits gameplay quality and can invalidate the court for competitive use. Adequate vertical space ensures unrestricted ball flight and a professional playing experience.
Failing to Match Court Size to Player Age and Skill Level
Using full-size court dimensions for young or beginner players can hinder development. Courts that are too large reduce engagement, increase fatigue, and discourage skill progression.
Youth courts should be scaled appropriately, with adjusted line distances and basket heights. Proper scaling improves learning, confidence, and long-term athletic development.
Neglecting Local and Organizational Regulations
Many courts fail to comply with local building codes or governing body standards. This oversight can lead to costly renovations, restricted usage, or disqualification from sanctioned events.
Ignoring regulations often results in:
- Inconsistent measurements
- Improper markings
- Safety violations
Verifying standards before construction prevents future complications and ensures long-term functionality.
Inconsistent Measurements During Installation
Even when correct dimensions are planned, poor execution during installation can create inconsistencies. Small measurement errors accumulate, leading to misaligned lines and distorted court geometry.
Professional layout, accurate tools, and verified measurements are essential to ensure precision. Consistency across all markings preserves fairness and enhances court quality.
Conclusion
Basketball court size is far more than a set of numbers; it is the foundation upon which the game is built. From professional arenas to neighborhood courts, precise dimensions and markings ensure fairness, safety, and consistency. Understanding these standards empowers players, coaches, and facility designers to create environments that support skill development and competitive excellence. As basketball continues to evolve globally, adherence to established court dimensions remains essential for preserving the integrity and excitement of the game.